What’s known
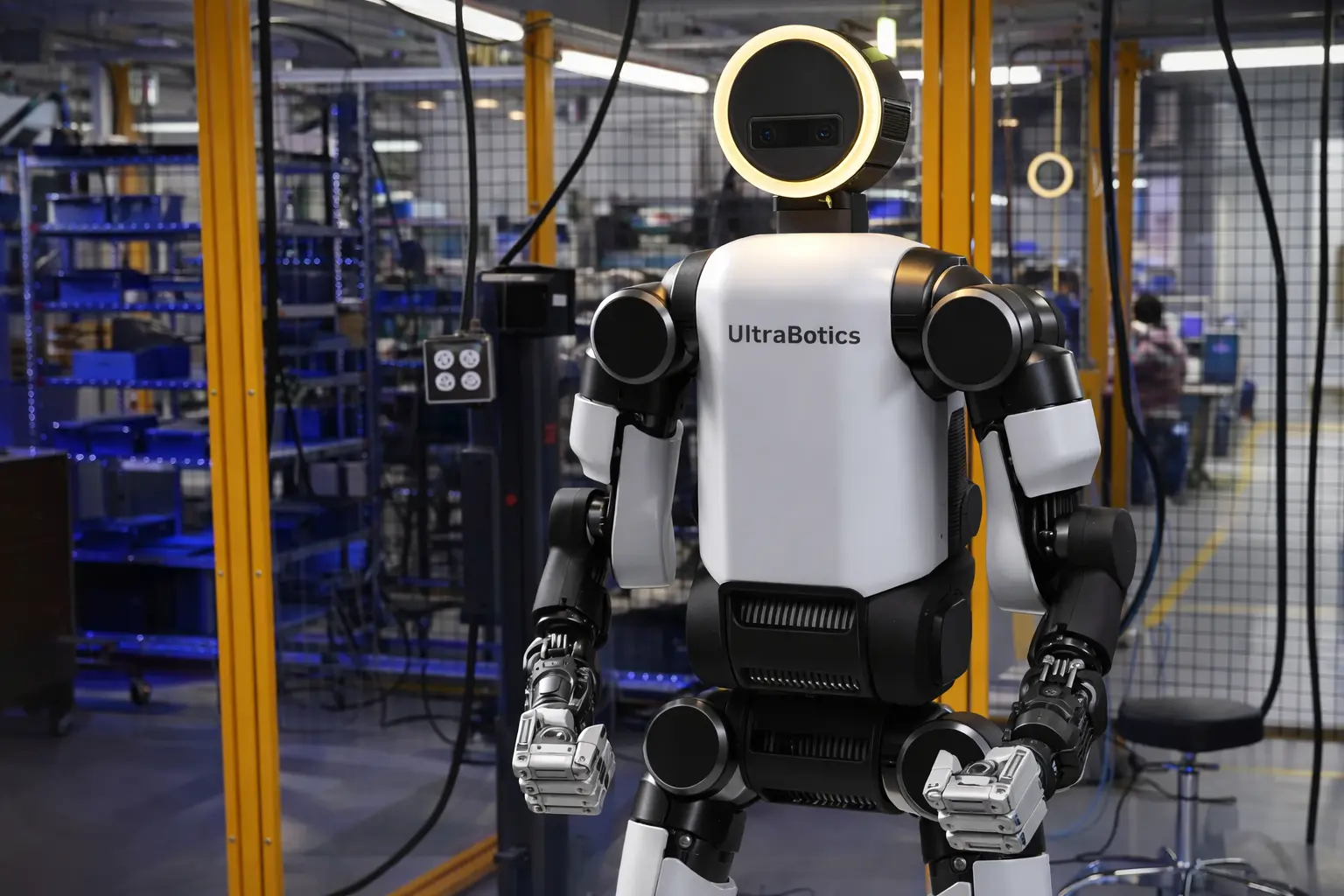
Atlas is designed for industrial applications. According to Boston Dynamics, the robot can operate autonomously, under direct operator control, or via a tablet-based interface. It is capable of lifting loads of up to 50 kg, has a reach of 2.3 meters, and can function in temperatures ranging from –20°C to +40°C.
Hyundai plans to begin deploying Atlas at its automotive manufacturing plants in 2028, initially for handling sequential component workflows. The company expects that by 2030, the robot will take on assembly tasks as well as jobs involving repetitive motions and the movement of heavy objects.
Google DeepMind will receive Atlas units to integrate its Gemini Robotics AI models into the robot’s control system. These models are expected to serve as the foundation for new use cases across a wide range of environments.
Development of Atlas began in 2011 as part of a DARPA program. In 2024, Boston Dynamics transitioned the robot from a hydraulic to a fully electric design. That same year, the company demonstrated Atlas’s ability to work with automotive components — a scenario that ultimately became the basis for its commercial deployment strategy.



 ES
ES  EN
EN