Google DeepMind has once again gone shopping in the AI startup market, closing several strategic deals this week to strengthen its technological capabilities.
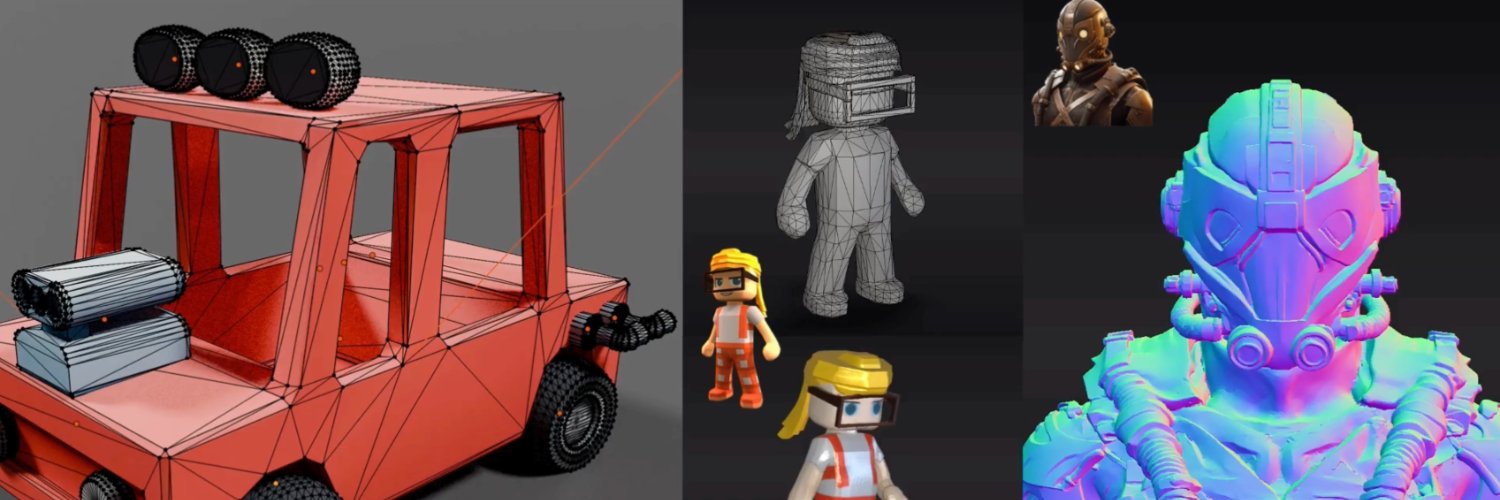
The tech giant has acquired Common Sense Machines, a Massachusetts-based startup with around twelve employees that develops AI models capable of converting 2D images into 3D objects. The company was last valued at $15 million, though the purchase price was not disclosed. Co-founder Tejas Kulkarni previously worked at Google DeepMind, and the entire team is expected to join DeepMind following the acquisition, according to The Information.

In parallel, Google signed a licensing agreement — effectively a soft acquisition — with Hume AI, a startup specializing in voice emotion recognition. Under the deal, Google receives non-exclusive rights to selected technologies. Hume AI CEO Alan Cowen and roughly seven engineers will move to DeepMind to enhance Gemini’s voice and emotional intelligence capabilities, Wired reports. Hume AI will continue operating independently and reportedly expects to generate $100 million in revenue this year, according to TechCrunch.
Google Invests in Research Lab Founded by Transformer Pioneers
Google also announced an investment in Sakana AI, a Tokyo-based research lab founded in 2023 and currently Japan’s most valuable AI startup, with a $2.5 billion valuation. Co-founder David Ha previously led Google Research in Japan, while Llion Jones was a co-author of Google’s original research paper that introduced the Transformer architecture.
Under the partnership, Sakana plans to combine Google’s AI models with its proprietary technologies — including the “AI Scientist” and “ALE Agent” systems — to accelerate AI-driven scientific discovery. The two companies also intend to develop advanced AI solutions for financial institutions and government agencies, focusing on the highest standards of security and data protection. The collaboration may strengthen Google’s competitive position in Japan’s rapidly growing AI market.
Sakana AI is also conducting research into alternatives to the current Transformer architecture, an area increasingly viewed as a key frontier in AI development. Another focus is the creation of self-improving autonomous agents. In a recent coding competition, Sakana’s code agent, powered by Gemini 2.5 Pro, ranked 21st among the world’s top 1,000 human programmers, underscoring the rapid progress of AI-assisted software development.
Conclusion:
Google’s latest moves show how aggressively the company is strengthening its AI ecosystem.



 ES
ES  EN
EN