“Kling 3.0 is built on a deeply unified training platform, enabling truly native multimodal input and output. Through seamless audio integration and advanced consistency control, the model brings a stronger sense of realism and coherence to generated content,” the company said in its announcement.
The model combines multiple capabilities, including converting text, images, and reference materials into video, as well as adding or removing content, and modifying or transforming existing clips.
Video length has been extended to 15 seconds. Other improvements include more flexible shot control and more accurate prompt adherence. Overall realism has also been enhanced, with character movements becoming more expressive and dynamic.
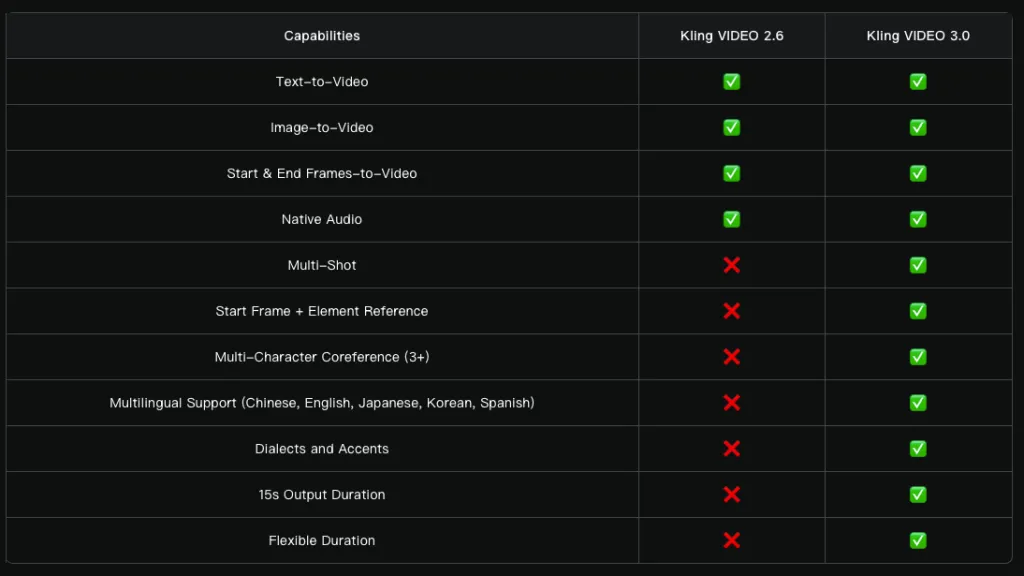
A new Multi-Shot feature analyzes prompts to determine scene structure and shot types, automatically adjusting camera angles and composition.
The model supports a wide range of editing styles—from classic shot–reverse-shot dialogues to parallel storytelling and scenes with voice-over narration.
“There’s no longer a need for tedious cutting and editing—one generation is enough to create a cinematic video and make complex audiovisual formats accessible to all creators,” the announcement said.
In addition to standard image-to-video generation, Kling 3.0 supports multiple image references and video inputs as scene elements.
The model locks in the characteristics of characters, objects, and scenes. Regardless of camera movement or narrative development, key elements remain stable and consistent throughout the video.
Native audio has also been upgraded: speech is synchronized more accurately with facial expressions, and in dialogue scenes users can manually specify the speaker.
The list of supported languages has expanded to include Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, and Spanish, with improved handling of dialects and accents.
In addition, the team upgraded its multimodal O1 model to Video 3.0 Omni.
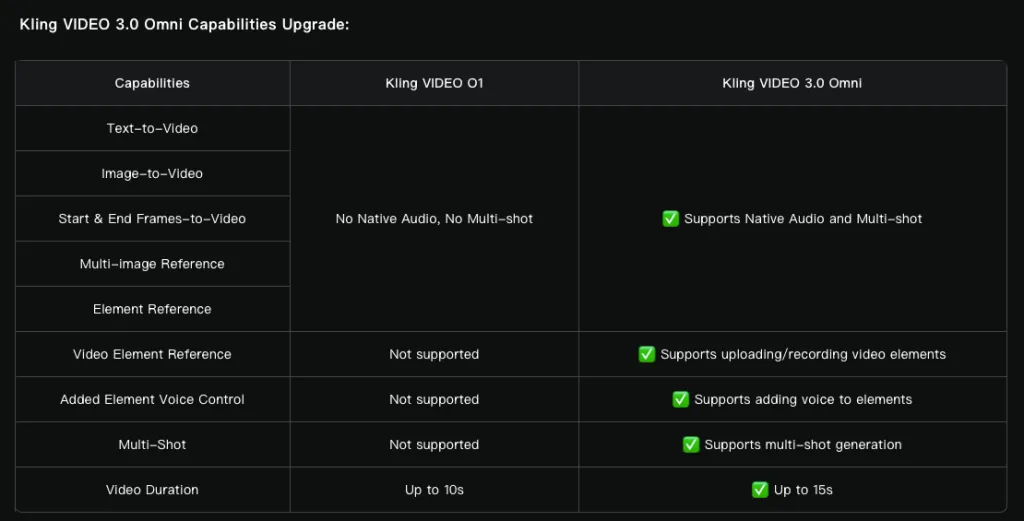
Users can upload audio clips with speech starting from three seconds to extract a voice, or provide three- to eight-second video clips of a character to capture its core attributes.
Competitors put pressure on Sora
OpenAI introduced its video generation model Sora in February 2024. The tool sparked excitement on social media, but a public release only followed in December.
Nearly a year later, users gained access to text-to-video generation, image animation, and video extension features.
The iOS version of Sora, released in September, quickly attracted attention, surpassing 100,000 downloads on its first day. It reached 1 million installs faster than ChatGPT, despite being invite-only.
However, the trend soon reversed. In December, downloads fell by 32% month over month, and the decline continued in January, with 1.2 million installs recorded.
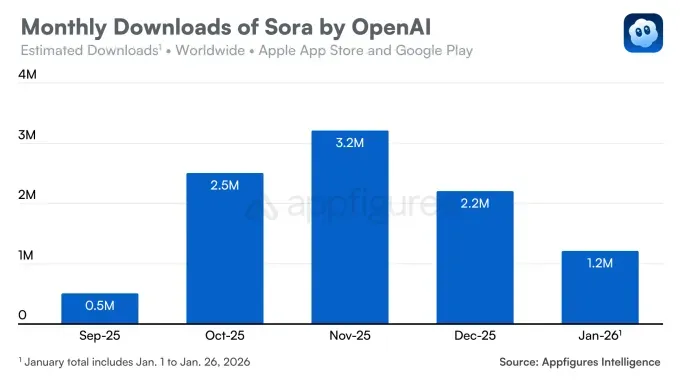
The slowdown was driven by several factors. First, competition intensified with Google’s Nano Banana model strengthening Gemini’s position. Sora also faces pressure from Meta AI and its Vibes feature, while Runway’s Gen-4.5 model raised the bar in independent tests.
Second, OpenAI encountered copyright challenges. Users generated videos featuring popular characters such as SpongeBob and Pikachu, forcing the company to tighten restrictions.
In December, the situation stabilized after OpenAI reached an agreement with Disney, allowing users to generate videos featuring the studio’s characters. However, this did not lead to renewed download growth.



 ES
ES  EN
EN